teams
Jun 24, 2025
Remote Team Project Management: Tools and Strategies That Actually Work
Remote Team Project Management: Tools and Strategies That Actually Work
Remote Team Project Management: Tools and Strategies That Actually Work
Remote teams don't fail because of distance—they fail because of coordination chaos. Discover the proven tools and strategies that enable distributed teams to outperform their office-bound competitors through visual-first project management and async-optimized workflows.
Remote teams don't fail because of distance—they fail because of coordination chaos. Discover the proven tools and strategies that enable distributed teams to outperform their office-bound competitors through visual-first project management and async-optimized workflows.
By Pete Cranston
By Pete Cranston
By Pete Cranston
Growth at Complex.so
Growth at Complex.so
Growth at Complex.so


18 min read
18 min read
Complex.so is calm task management for real work
No separate docs. No noise. No unnecessary features.
Try it for free
Remote teams don't fail because of distance—they fail because of coordination chaos.
The shift to distributed work has exposed a fundamental truth: traditional project management approaches crumble when teams spread across time zones. While 58% of the American workforce now has access to remote work options, most organizations still rely on project management strategies designed for conference rooms and cubicles.
This disconnect creates real coordination challenges. While recent Project Management Institute research shows remote teams achieve similar success rates to in-person teams (73.2% vs 74.6%), they face unique obstacles including communication overhead and visibility gaps that require different management approaches. The tools that worked for in-person collaboration—impromptu desk visits, whiteboard sessions, and hallway conversations—simply don't translate to distributed environments.
Remote work has evolved from emergency pandemic response to strategic business choice. Companies embracing distributed teams access global talent pools, reduce overhead costs, and offer flexibility that attracts top performers. However, success requires fundamentally different project management approaches.
Remote team project management isn't about replicating office dynamics through video calls and chat apps. It's about building systems that thrive on asynchronous communication, visual clarity, and results-oriented accountability. The teams that master these principles don't just survive remote work—they outperform their office-bound competitors.
The stakes are high. Organizations that nail remote project management gain competitive advantages: faster hiring, lower costs, and access to global expertise. Those that don't face constant firefighting, missed deadlines, and team member burnout from coordination overhead.
This guide reveals the tools and strategies that actually work for distributed teams. You'll discover why remote teams need different approaches, what separates successful remote project management from office-based coordination, and how to implement systems that deliver results regardless of where your team members work.
According to McKinsey research, 58% of the American workforce now has access to remote work options, representing about 92 million workers with flexible work capability.
Why Remote Teams Need Different Project Management
Communication Overhead Multiplication
Remote work transforms simple conversations into complex coordination challenges. What takes thirty seconds at someone's desk becomes email threads, delayed responses, and decision bottlenecks. Microsoft Teams data shows a 200% increase in meeting minutes during the initial remote work transition, highlighting how teams struggle to recreate informal information flow in distributed environments.
Time zone differences amplify these challenges exponentially. A decision that requires input from team members in New York, London, and Singapore can take 24-48 hours instead of 24 minutes. This delay cascades through project timelines, creating compounding coordination costs that office-based teams never experience.
The loss of peripheral awareness—knowing what others are working on through visual and auditory cues—forces remote teams to create explicit communication systems. Without deliberate coordination structures, information silos develop quickly, leading to duplicated work, missed dependencies, and strategic misalignment.

Visibility and Transparency Requirements
In physical offices, project status lives in observable behaviors: busy team members, progress on whiteboards, and informal updates during coffee breaks. Remote environments eliminate these ambient status indicators, making project visibility an intentional design challenge rather than automatic byproduct.
Traditional project management assumes status can be gathered through informal check-ins and observation. Remote teams need self-service status systems where any team member can understand project progress, task ownership, and upcoming deadlines without scheduling meetings or sending emails.
Documentation shifts from helpful supplement to critical infrastructure. Decisions, rationale, and context that would normally transfer through conversation must be captured systematically. Remote teams that treat documentation as optional experience constant context reconstruction, slowing progress and frustrating team members.
Trust and Accountability Dynamics
Remote work requires fundamental shifts from time-based to results-based evaluation. Without physical presence indicators, accountability must center on deliverables, milestones, and outcomes rather than hours worked or meetings attended. This transition challenges traditional management approaches built on observation and presence.
Clear deliverable definitions become essential rather than nice-to-have. Ambiguous task descriptions that might get clarified through quick conversations in office settings create significant delays in remote environments. Every task needs explicit success criteria, deadlines, and ownership to prevent coordination failures.
The trust required for remote work extends beyond personal relationships to system confidence. Team members need to trust that important information will be captured and accessible, that their contributions are visible to stakeholders, and that project coordination won't require constant individual effort to maintain visibility.
Tool Complexity Costs
Learning curves amplify dramatically in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events. Tools that seem intuitive during in-person demonstrations often confuse team members working independently. Complex interfaces that office workers might navigate through peer assistance become productivity barriers for remote teams.
Remote workers operate in distraction-rich environments where focus time is precious. Project management tools that require extensive navigation, multiple screens, or complex setup processes interrupt deep work unnecessarily. Simple, visual interfaces become competitive advantages rather than aesthetic preferences.
The cost of tool switching multiplies for remote teams juggling multiple communication platforms, project trackers, and coordination systems. Each additional tool creates cognitive overhead and increases the likelihood of missed information or fragmented communication. This is why choosing simple project management tools becomes crucial for remote team success.
Remote Team Project Management Challenges
Time Zone Coordination Nightmares
Scheduling across multiple time zones transforms simple coordination into complex optimization problems. Finding meeting times that work for team members in California, New York, London, and Mumbai often means someone joins at inconvenient hours or misses critical discussions entirely.
Decision-making delays become project killers when approvals require input from stakeholders across different continents. What should be quick decisions stretch into multi-day processes, creating bottlenecks that cascade through project timelines and frustrate team members waiting for direction.
Follow-the-sun workflows, where projects move continuously across time zones, require sophisticated handoff procedures and documentation standards. Without proper coordination systems, work stops at regional boundaries rather than flowing smoothly around the clock.
Meeting fatigue hits remote teams particularly hard when attempting to accommodate global schedules. The constant compromise of inconvenient meeting times leads to reduced participation, poor decision quality, and team member resentment about work-life balance disruption.

Information Silos and Knowledge Gaps
The tribal knowledge that develops naturally through office interactions—knowing who to ask about specific topics, understanding project history, and awareness of upcoming changes—disappears in remote environments without systematic knowledge management.
Documentation becomes critical infrastructure, but most teams treat it as administrative overhead rather than core productivity tool. Important decisions made in video calls or chat conversations often remain undocumented, creating knowledge gaps for team members who weren't present or joined later.
Onboarding new remote team members requires deliberate knowledge transfer processes that many organizations haven't developed. New hires struggle to understand project context, team dynamics, and informal procedures that office workers absorb through osmosis.
Context sharing for complex projects becomes exponentially more difficult when explanations can't happen through quick screen sharing or whiteboard sketches. Remote teams need project management tools that capture and communicate context visually and accessibly.
Accountability and Progress Tracking
Work visibility challenges make traditional management approaches ineffective for remote teams. Managers can't gauge productivity through observation, requiring new systems for understanding individual and project progress without micromanagement.
Results measurement becomes essential when time tracking loses relevance. Remote teams need clear milestone definitions, deliverable specifications, and success criteria that enable autonomous work while maintaining accountability to team and organizational goals.
Performance evaluation complexities multiply when traditional indicators—meeting participation, office presence, and informal collaboration—no longer apply. Remote team performance must be measured through output quality, deadline adherence, and contribution to team objectives.
Tool Overload and Integration Issues
Multiple communication channels create information fragmentation where important updates get lost in chat streams, email threads, and project platform notifications. Remote teams often struggle to maintain single sources of truth across their technology stack.
Platform switching fatigue reduces productivity when team members must navigate between email, chat apps, project trackers, file storage, and video conferencing tools to complete basic work coordination. Each tool switch interrupts focus and increases cognitive load.

Integration complexity often requires technical knowledge that small remote teams lack. Connecting project management tools with communication platforms, calendar systems, and file storage requires configuration effort that becomes barrier to adoption rather than productivity enhancement.
Cost accumulation from multiple tool subscriptions hits small remote teams particularly hard. What starts as necessary communication tools often grows into expensive software stack that exceeds budget constraints without delivering proportional productivity benefits. This is especially challenging for small teams seeking project management software under $10 per user.
What Remote Teams Actually Need from PM Tools
Visual Clarity and Immediate Understanding
Remote teams require project management tools that communicate status instantly without requiring navigation, interpretation, or additional context. At-a-glance understanding becomes critical when team members work asynchronously across different time zones and can't ask quick clarifying questions.
Visual progress indicators must work across cultural and linguistic differences. Color coding, progress bars, and status symbols communicate more effectively than text descriptions when team members speak different languages or work in varying cultural contexts.
Intuitive information architecture enables self-service updates where team members can find relevant project information without disturbing colleagues or waiting for responses. Clear navigation and logical organization reduce coordination overhead that kills remote productivity.
Task ownership and deadline visibility needs to be immediately apparent to everyone involved. Remote teams can't rely on informal awareness of who's working on what—this information must be explicit and constantly accessible to prevent confusion and duplicated effort.
Async-First Communication Design
Threaded conversations tied to specific tasks and projects preserve context for team members who join discussions later or work in different time zones. Unlike general chat platforms where important information gets buried in conversation streams, task-specific communication maintains relevance and searchability.
Status update automation reduces manual reporting overhead that exhausts remote team members. Tools that capture progress automatically through task completion, milestone achievement, and deadline updates eliminate redundant status meetings and administrative busywork.
Context preservation for decisions made across time zones ensures that rationale, alternatives considered, and implementation details remain accessible long after initial discussions. Remote teams need searchable decision history that enables informed future choices.
Notification intelligence respects time zones and work hours to prevent communication overload while ensuring urgent information reaches relevant team members promptly. Smart filtering and scheduling reduce interruption while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Simple Onboarding for Distributed Teams
Self-service team member addition eliminates administrative bottlenecks when new people join projects. Remote teams need tools that enable immediate productivity without requiring extensive setup procedures or training sessions across time zones.
Intuitive interfaces reduce training requirements to absolute minimum. When quick questions become formal communication events, tools must be self-explanatory enough that team members can become productive independently without extensive guidance.
Template-based project setup creates consistency across team practices while reducing setup time for new initiatives. Standard structures help distributed teams maintain coordination patterns that work across different projects and team compositions.
Mobile accessibility ensures team members can stay connected and productive regardless of location or device availability. Remote work often involves varied work environments where desktop access isn't guaranteed.
Integration with Remote Work Stack
Calendar synchronization connects project deadlines with individual schedules, enabling realistic timeline planning that accounts for team member availability across different time zones and work patterns.
File sharing integration with cloud storage solutions reduces platform switching and ensures project documents remain accessible from within project management context. Seamless connections prevent information silos between storage and coordination systems.
Communication tool connectivity enables project updates to flow into existing team communication channels without requiring separate platform monitoring. Integration reduces tool fragmentation while maintaining notification effectiveness.
Time zone awareness in scheduling and deadline features prevents coordination mistakes that happen when global teams work with tools designed for single-location use. Automatic time zone conversion and scheduling assistance reduce coordination complexity.
Cost Efficiency for Small Remote Teams
Transparent pricing structures help small teams budget effectively without surprise costs from additional features, integrations, or user additions. Remote teams often operate with tight budgets where unexpected expenses create significant problems.
Scalable costs that grow reasonably with team size enable organic growth without requiring major tool transitions as organizations expand. Pricing flexibility supports remote teams through different growth phases.
No hidden integration fees or setup costs prevent budget surprises that small teams can't absorb. Clear, predictable pricing enables confident tool adoption and long-term planning.
Value optimization over feature maximization recognizes that small remote teams need tools that solve core coordination problems effectively rather than comprehensive feature sets they'll never use.

Complex.so: Purpose-Built for Remote Team Reality
Visual-First Remote Collaboration
Complex.so solves remote team coordination through immediate visual understanding that works across time zones, languages, and cultural differences. Project status becomes instantly clear through color-coded organization and progress indicators that eliminate the need for status meetings or lengthy email updates.
The platform's visual task boards communicate project state at a glance, enabling team members to understand priorities, deadlines, and dependencies without navigating complex menus or interpreting text-heavy interfaces. This visual clarity reduces coordination overhead that typically consumes remote team productivity.
Progress tracking happens automatically through visual indicators that update as team members complete tasks and reach milestones. Remote teams can see project advancement in real-time without requiring manual status reports or constant communication about individual progress.
The interface design prioritizes information density that enables comprehensive project understanding from single screen views. Remote team members can assess project status, identify bottlenecks, and understand next steps without switching between multiple views or platforms.
Async Communication Excellence
Task-level commenting preserves conversation context directly within project structure, eliminating the information fragmentation that plagues remote teams using separate communication tools. Discussions remain connected to relevant work, making decision history searchable and accessible.
@mention functionality respects time zones and work schedules, ensuring important communications reach relevant team members without creating notification overload. Smart notification timing reduces interruptions while maintaining coordination effectiveness across global teams.
Automated status updates eliminate redundant reporting that exhausts remote team members. Progress flows naturally through task completion and milestone achievement, providing stakeholders with current information without requiring manual coordination effort.
The platform captures decision rationale and project context automatically as teams work, creating searchable knowledge bases that prevent information loss common in remote environments. This systematic context preservation supports long-term project success and team member onboarding.
5-Minute Remote Onboarding
New team members become productive immediately through intuitive interface design that requires no training sessions across time zones. The platform's self-explanatory structure enables independent adoption without extensive guidance or documentation.
No complex setup procedures delay team member integration into ongoing projects. Simple invitation and immediate access eliminate onboarding friction that often prevents quick team scaling in remote environments.
Mobile applications provide identical functionality to desktop versions, ensuring team members can contribute effectively regardless of location or device availability. Consistent experience across platforms supports flexible work arrangements without productivity compromise.
The Buffer State of Remote Work 2023 report found that 98% of remote workers want to continue working remotely for the rest of their careers, with 36% saying career growth is easier remotely compared to just 14% in 2022.
Small Remote Team Economics
Pricing transparency eliminates budget surprises that small remote teams can't absorb. Clear, predictable costs enable confident adoption and long-term financial planning without fear of unexpected expenses from feature additions or integrations.
The platform replaces multiple tools commonly used by remote teams—task management, communication threading, file organization, and progress reporting—providing economic efficiency through consolidated functionality rather than expensive tool stack accumulation.
Scalable pricing grows reasonably with team expansion, supporting remote organizations through different growth phases without requiring disruptive tool transitions. Economic flexibility enables organic team development without productivity interruption.
No per-integration fees or hidden costs prevent the budget escalation that commonly affects small teams adopting multiple remote work tools. Comprehensive functionality within single subscription supports predictable financial planning.
Global Team Considerations
Time zone aware scheduling and deadline features prevent coordination mistakes common when global teams use tools designed for single-location use. Automatic time zone conversion and intelligent scheduling reduce coordination complexity across distributed teams.
The platform's performance remains consistent across different internet conditions and geographic locations, ensuring reliable access for team members regardless of local infrastructure quality. Global reliability supports truly distributed team collaboration.
Multi-language interface support and cultural communication pattern accommodation enable effective coordination across diverse teams without requiring common language proficiency for tool navigation and basic project coordination.
Notification intelligence respects cultural work patterns and local holiday schedules, ensuring communication effectiveness while maintaining appropriate work-life boundaries across different regions and time zones.
Remote PM Tool Comparison for Small Teams
Complex.so: The Remote-Optimized Choice
Complex.so addresses remote team challenges through design decisions specifically optimized for distributed collaboration. Visual clarity reduces coordination overhead, async-first communication preserves context across time zones, and simple onboarding eliminates training barriers that delay productivity.
The platform's remote advantages stem from recognizing that distributed teams need fundamentally different coordination approaches than office-based groups. Rather than adapting office-designed tools for remote use, Complex.so builds collaboration patterns that leverage remote work strengths while mitigating inherent challenges.
Small remote teams (5-15 people) achieve immediate productivity without extensive configuration, training periods, or integration complexity. The tool works effectively from day one, enabling focus on project outcomes rather than coordination mechanics.
Economic efficiency comes through consolidated functionality that replaces multiple tools commonly required for remote team coordination. Single subscription provides task management, communication threading, progress tracking, and file organization without additional integration costs.
Asana: Feature-Rich but Complex for Remote
Asana provides comprehensive project management features that appeal to larger organizations with dedicated project management resources. Robust reporting, advanced workflow automation, and extensive customization options support complex project requirements and organizational scaling.
Remote challenges emerge through interface complexity that requires extensive training for effective adoption. The learning curve amplifies in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events, delaying productivity and frustrating team members.
While Asana works well for larger remote teams with dedicated project managers who can handle configuration and training responsibilities, small distributed teams often struggle with adoption complexity that exceeds their coordination benefits.
The platform's extensive feature set can overwhelm small teams who need immediate coordination solutions rather than comprehensive project management infrastructure requiring ongoing administration and optimization.
Trello: Simple but Limited for Remote Coordination
Trello's card-based interface provides intuitive visual organization that works well for basic project coordination and simple task tracking. The simplicity appeals to small teams who need immediate adoption without complex setup procedures.
Remote limitations become apparent when projects require advanced coordination features like time tracking, reporting, dependency management, or integrated communication. The platform's simplicity becomes constraint rather than advantage for complex remote project requirements.
Very small teams with straightforward project needs may find Trello sufficient for basic coordination, but growing remote teams typically outgrow the platform's capabilities as project complexity increases and coordination requirements become more sophisticated.
Integration limitations prevent seamless workflow connections with other remote work tools, creating information silos and platform switching overhead that reduces productivity for distributed teams.

Monday.com: Powerful but Overwhelming for Remote Teams
Monday.com provides highly customizable project management infrastructure with advanced features for complex workflow automation, detailed reporting, and extensive integration capabilities appealing to larger organizations with sophisticated project requirements.
Remote challenges include overwhelming complexity that requires extensive setup and ongoing administration. The platform's power becomes liability for small remote teams who need immediate productivity rather than comprehensive configuration projects.
Training overhead amplifies in remote environments where team members must learn complex interfaces independently without immediate peer assistance. The sophisticated feature set often exceeds small team needs while creating adoption barriers.
Cost complexity through numerous add-ons and feature tiers makes budget planning difficult for small remote teams operating with constrained resources and predictable expense requirements.
Slack/Teams + Basic PM: Communication-Heavy Approach
Combining communication platforms with basic project management creates fragmented coordination where project information spreads across chat streams, shared documents, and simple task lists without integrated structure or searchable organization.
Information gets lost in conversation streams where important project updates, decisions, and deadlines become buried in ongoing chat activity. Retrieving project context requires searching through conversation history rather than accessing organized project structure.
The approach fails to provide visual project overview or systematic progress tracking, forcing remote teams to rely on manual status updates and constant communication for coordination rather than self-service information access.
No structured project organization means task dependencies, milestone tracking, and resource allocation remain invisible, preventing strategic project planning and creating coordination chaos for anything beyond simple task lists.
Remote Team PM Implementation Strategy
Phase 1: Tool Selection and Setup (Week 1)
Begin implementation by evaluating project management tools using remote-specific criteria rather than general feature comparisons. Prioritize visual clarity, async communication capabilities, and simple onboarding over comprehensive feature sets that require extensive configuration.
Focus evaluation on tools that work immediately for distributed teams without requiring training sessions across time zones or complex setup procedures. Test core functionality with actual project scenarios rather than demo environments to understand real-world usability.
Set up initial project structure using basic templates that reflect your team's work patterns. Create sample projects that demonstrate typical workflows while establishing naming conventions and organizational standards that support scalable adoption.
Invite team members gradually to test core functionality with pilot projects before full implementation. This phased approach identifies usability issues and adoption barriers while building confidence through successful early experiences.
Phase 2: Team Onboarding and Training (Week 2)
Schedule onboarding sessions that accommodate different time zones without requiring everyone to attend simultaneously. Create recorded training materials that team members can access independently, reducing coordination overhead while ensuring consistent information transfer.
Develop documentation focused on common use cases and frequently asked questions rather than comprehensive feature explanations. Remote team members need quick reference materials for independent problem-solving rather than exhaustive training manuals.
Start implementation with simple projects that demonstrate value without overwhelming team members with advanced features. Success with basic coordination builds confidence for adopting more sophisticated functionality as comfort levels increase.
Establish communication norms around tool usage, notification preferences, and update frequencies. Clear expectations prevent coordination confusion while respecting individual work patterns and time zone constraints.
Phase 3: Workflow Optimization (Weeks 3-4)
Refine notification settings based on team feedback about communication effectiveness versus interruption frequency. Optimize alert timing and filtering to maintain coordination without creating notification overload that disrupts focus time.
Establish async update rhythms that provide stakeholders with progress information without requiring manual reporting overhead. Automate status communication through milestone completion and deadline achievement rather than scheduled status meetings. Learn more about effective team task management approaches for distributed teams.
Create project templates that capture successful coordination patterns for reuse across similar initiatives. Standardized structures reduce setup time while maintaining flexibility for project-specific requirements and team preferences.
Develop documentation standards that capture decision rationale and context for future reference. Systematic knowledge preservation prevents information loss common in remote environments where informal communication doesn't happen naturally.
Phase 4: Advanced Features and Integration (Month 2)
Integrate project management tools with existing remote work technology stack to reduce platform switching and information fragmentation. Connect calendar systems, communication tools, and file storage to create seamless workflow continuity.
Implement advanced reporting that provides stakeholders with project insights without requiring manual data compilation. Automated progress summaries and trend analysis support strategic decision-making while reducing administrative overhead.
Establish productivity metrics that focus on outcomes rather than activity levels. Track milestone achievement, deadline adherence, and deliverable quality rather than time spent or meetings attended to support results-oriented remote work culture.
Research from Stanford's Nicholas Bloom demonstrates that remote work can increase productivity by 13% when properly implemented with structured coordination systems.
Remote Team PM Best Practices
Async-First Communication
Default to asynchronous communication methods that enable thoughtful responses rather than immediate reactions. Reserve synchronous meetings for complex decision-making, creative collaboration, and relationship building rather than routine information sharing.
Use threaded conversations that preserve context and enable team members to join discussions regardless of time zone constraints. Task-specific communication threads maintain relevance while preventing important information from getting lost in general conversation streams.
Establish response time expectations that balance coordination needs with deep work protection. Clear expectations about urgent versus routine communication prevent anxiety while ensuring important information receives appropriate attention across time zones.
Document decisions and rationale systematically rather than relying on meeting notes or chat conversations. Searchable decision history enables informed future choices while providing context for team members who weren't present during initial discussions.
Documentation and Context Sharing
Create searchable project knowledge bases that capture institutional memory and prevent information loss when team members change or projects evolve. Systematic documentation reduces dependency on individual knowledge while supporting long-term project success.
Maintain clear project history that includes decision rationale, alternative options considered, and implementation details. Comprehensive context helps future team members understand project evolution while supporting informed modification and expansion decisions.
Develop information architecture that enables self-service knowledge discovery. Organized, searchable documentation reduces coordination overhead while ensuring team members can find relevant information independently without interrupting colleagues.
Update documentation systematically as projects evolve rather than treating it as one-time activity. Living documentation that reflects current project state provides ongoing value while preventing knowledge decay common in fast-moving remote environments.
Results-Oriented Accountability
Focus performance evaluation on deliverable quality, milestone achievement, and contribution to team objectives rather than activity indicators like meeting attendance or hours worked. Results-based accountability aligns with remote work strengths while supporting autonomous work styles.
Define success criteria explicitly for every task and milestone to eliminate ambiguity that creates coordination problems in remote environments. Clear expectations enable autonomous work while maintaining alignment with project objectives and team standards.
Implement regular but non-overwhelming progress check-ins that focus on obstacle identification and resource needs rather than detailed status reporting. Strategic support conversations add value while avoiding micromanagement that undermines remote work benefits.
According to GitLab's annual remote work report, 84% of employees report feeling more productive in remote and hybrid work models when proper coordination tools and practices are implemented.
Tool Simplicity and Adoption
Choose project management tools that provide immediate value without requiring extensive configuration or training periods. Prioritize intuitive interfaces and self-explanatory functionality over comprehensive feature sets that create adoption barriers.
Avoid tool proliferation that creates context switching overhead and information fragmentation. Consolidate functionality through integrated platforms rather than accumulating specialized tools that complicate workflow and increase cognitive load.
Prioritize visual clarity that communicates project status instantly without requiring navigation or interpretation. At-a-glance understanding reduces coordination overhead while supporting effective async collaboration across time zones and cultural differences.
Test tool adoption with actual team members in realistic work environments rather than relying on demonstration environments or feature lists. Real-world usability often differs significantly from controlled testing scenarios.
Global Team Considerations
Respect cultural communication preferences and work pattern differences when establishing team coordination norms. Flexible approaches that accommodate cultural diversity create inclusive environments while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Plan project timelines that account for different holiday schedules and cultural observances across team locations. Global awareness prevents coordination problems while demonstrating respect for team member cultural commitments.
Use time zone aware tools and scheduling practices that distribute coordination burden fairly rather than consistently favoring particular geographic regions. Equitable coordination builds team cohesion while preventing resentment from unfair schedule accommodations.
Consider language and cultural context when creating documentation and communication standards. Clear, accessible communication reduces misunderstanding while supporting effective collaboration across diverse global teams.
Common Remote PM Mistakes to Avoid
Over-Communication Compensation
Many remote teams attempt to recreate office-level visibility through excessive status meetings and constant check-ins. This over-correction creates meeting fatigue while interrupting the deep work that makes remote environments productive.
Information overload through multiple communication channels often makes coordination less effective rather than more transparent. Teams that maintain separate streams for email, chat, project updates, and meeting notes create fragmentation that reduces rather than improves visibility.
The temptation to replicate in-person communication patterns through video calls and chat conversations often misses opportunities to leverage async communication strengths. Remote teams thrive when they embrace asynchronous coordination rather than fighting against time zone differences.
Status reporting that requires manual effort from team members creates administrative overhead that reduces productivity. Automated progress tracking through task completion and milestone achievement provides better visibility with less effort.

Tool Complexity Underestimation
Choosing feature-rich project management platforms often creates adoption barriers that prevent effective team coordination. Complex interfaces require training investments that small remote teams often can't make, leading to partial adoption and coordination failures. This is why enterprise project management tools often fail small teams.
Underestimating learning curve impact in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events leads to prolonged productivity reduction. Tools that seem intuitive during sales demonstrations often confuse team members working independently.
Integration complexity that requires technical knowledge often prevents small remote teams from connecting their tool stack effectively. Sophisticated connection capabilities become worthless when teams lack resources to implement and maintain integrations.
Feature addiction leads teams to choose tools based on capability lists rather than actual usage requirements. Comprehensive platforms often overwhelm small teams while creating administrative overhead that exceeds coordination benefits.
One-Size-Fits-All Approaches
Applying in-office project management practices to remote teams ignores fundamental differences in communication patterns, coordination requirements, and work styles. Remote teams need strategies designed for distributed collaboration rather than adapted office approaches.
Assuming global teams can accommodate single time zone scheduling creates unfair burden distribution and reduces participation from team members in inconvenient time zones. Successful remote coordination requires flexible approaches that distribute inconvenience equitably.
Using communication tools designed for co-located teams often creates information fragmentation and reduces async collaboration effectiveness. Remote-optimized tools provide better coordination outcomes than general-purpose communication platforms.
Ignoring cultural communication preferences and work pattern differences creates coordination friction that reduces team effectiveness. Global teams need flexible coordination approaches that accommodate cultural diversity while maintaining project alignment.
Neglecting Onboarding for Remote Context
Insufficient documentation for self-service learning creates dependency on individual knowledge that becomes coordination bottleneck when team members are unavailable across time zones. Remote teams need comprehensive, searchable knowledge bases for independent problem-solving.
Assuming new team members can ask questions easily ignores the communication overhead that makes simple clarifications into formal events in remote environments. Thorough onboarding materials reduce coordination burden while accelerating productivity.
Failing to provide project context and decision history leaves new team members without institutional knowledge that office workers acquire through informal observation and conversation. Systematic context sharing supports effective remote team integration.
Inadequate tool training that assumes intuitive adoption often leads to partial usage and coordination problems. Remote team members need self-paced training materials and clear usage examples for effective tool adoption without time zone coordination requirements.
FAQ Section
How do you maintain accountability with remote teams?
Accountability in remote teams comes through clear deliverable definitions, milestone-based progress tracking, and results-oriented evaluation rather than activity monitoring. Focus on output quality and deadline adherence rather than hours worked or meeting participation.
Establish explicit success criteria for every task and project milestone to eliminate ambiguity that creates coordination problems. Regular but non-overwhelming check-ins should focus on obstacle identification and resource needs rather than detailed status reporting.
Use project management tools that provide visibility into progress and contribution without requiring manual reporting overhead. Automated status updates through task completion and milestone achievement maintain accountability while respecting autonomous work styles.
Document decisions and maintain project history to create accountability through transparency rather than surveillance. Searchable records of contributions and decisions support fair evaluation while building institutional knowledge.
What's the best way to handle time zone differences in project management?
Time zone coordination requires tools and practices designed for asynchronous collaboration rather than attempting to find universal meeting times. Prioritize async communication methods that enable thoughtful participation regardless of local time constraints.
Use project management platforms with time zone awareness that automatically convert deadlines and scheduling information for individual team members. Avoid coordination mistakes through tools that handle time zone complexity automatically.
Establish follow-the-sun workflows where projects move continuously across time zones with proper handoff procedures and documentation standards. Create systematic knowledge transfer processes that enable work continuity without requiring overlap hours.
Distribute coordination burden equitably rather than consistently favoring particular geographic regions. Rotate meeting times and deadline accommodations to prevent unfair schedule impact on specific team members.
How do you onboard new team members to PM tools remotely?
Remote onboarding requires comprehensive self-service materials that enable independent learning without real-time guidance across time zones. Create recorded training sessions, documentation, and usage examples that new team members can access at convenient times.
Start with simple projects that demonstrate core functionality before introducing advanced features. Success with basic coordination builds confidence while preventing overwhelming complexity during initial adoption period.
Provide project templates and usage examples that reflect actual work patterns rather than theoretical scenarios. Real-world context helps new team members understand tool application to their specific responsibilities and project requirements.
Assign onboarding buddies in compatible time zones who can provide guidance and answer questions without requiring coordination across inconvenient hours. Peer support accelerates adoption while building team relationships.
Should remote teams use different tools than in-office teams?
Remote teams benefit from tools specifically designed for distributed collaboration rather than adapted office-based solutions. Visual clarity, async communication capabilities, and simple onboarding become critical factors that aren't as important for co-located teams. Consider exploring no-code project management solutions for easier adoption.
Prioritize platforms that provide at-a-glance project understanding and self-service information access. Remote teams can't rely on informal awareness and quick questions that happen naturally in shared physical spaces.
Choose tools with mobile optimization and reliable performance across different internet conditions since remote team members work in varied environments with different technology constraints.
Consider economic efficiency more carefully since remote teams often operate with distributed budget authority and need predictable costs rather than enterprise pricing structures designed for centralized purchasing decisions.
How do you prevent remote team communication overload?
Communication overload prevention requires strategic tool selection that consolidates information streams rather than fragmenting coordination across multiple platforms. Choose integrated solutions that provide project coordination within single interface.
Establish notification intelligence that respects time zones and work schedules while ensuring urgent information reaches relevant team members promptly. Smart filtering reduces interruption while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Default to async communication methods that enable thoughtful responses rather than immediate reactions. Reserve synchronous meetings for complex decision-making and creative collaboration rather than routine information sharing.
Create clear communication norms around urgency levels, response time expectations, and appropriate channels for different types of information. Explicit guidelines prevent anxiety while ensuring important coordination doesn't get lost in routine updates.
Ready to streamline your remote team's project management? Try Complex.so free for 14 days and discover how visual-first coordination transforms distributed team productivity. No credit card required, no complex setup—just immediate organization that works across time zones.
Looking for more remote team strategies? Explore our complete guide to small team collaboration tools, discover 5 project management tips specifically for small teams, and learn about building high-performing remote teams. For teams just getting started, check out our 5-minute setup guide.
Remote teams don't fail because of distance—they fail because of coordination chaos.
The shift to distributed work has exposed a fundamental truth: traditional project management approaches crumble when teams spread across time zones. While 58% of the American workforce now has access to remote work options, most organizations still rely on project management strategies designed for conference rooms and cubicles.
This disconnect creates real coordination challenges. While recent Project Management Institute research shows remote teams achieve similar success rates to in-person teams (73.2% vs 74.6%), they face unique obstacles including communication overhead and visibility gaps that require different management approaches. The tools that worked for in-person collaboration—impromptu desk visits, whiteboard sessions, and hallway conversations—simply don't translate to distributed environments.
Remote work has evolved from emergency pandemic response to strategic business choice. Companies embracing distributed teams access global talent pools, reduce overhead costs, and offer flexibility that attracts top performers. However, success requires fundamentally different project management approaches.
Remote team project management isn't about replicating office dynamics through video calls and chat apps. It's about building systems that thrive on asynchronous communication, visual clarity, and results-oriented accountability. The teams that master these principles don't just survive remote work—they outperform their office-bound competitors.
The stakes are high. Organizations that nail remote project management gain competitive advantages: faster hiring, lower costs, and access to global expertise. Those that don't face constant firefighting, missed deadlines, and team member burnout from coordination overhead.
This guide reveals the tools and strategies that actually work for distributed teams. You'll discover why remote teams need different approaches, what separates successful remote project management from office-based coordination, and how to implement systems that deliver results regardless of where your team members work.
According to McKinsey research, 58% of the American workforce now has access to remote work options, representing about 92 million workers with flexible work capability.
Why Remote Teams Need Different Project Management
Communication Overhead Multiplication
Remote work transforms simple conversations into complex coordination challenges. What takes thirty seconds at someone's desk becomes email threads, delayed responses, and decision bottlenecks. Microsoft Teams data shows a 200% increase in meeting minutes during the initial remote work transition, highlighting how teams struggle to recreate informal information flow in distributed environments.
Time zone differences amplify these challenges exponentially. A decision that requires input from team members in New York, London, and Singapore can take 24-48 hours instead of 24 minutes. This delay cascades through project timelines, creating compounding coordination costs that office-based teams never experience.
The loss of peripheral awareness—knowing what others are working on through visual and auditory cues—forces remote teams to create explicit communication systems. Without deliberate coordination structures, information silos develop quickly, leading to duplicated work, missed dependencies, and strategic misalignment.

Visibility and Transparency Requirements
In physical offices, project status lives in observable behaviors: busy team members, progress on whiteboards, and informal updates during coffee breaks. Remote environments eliminate these ambient status indicators, making project visibility an intentional design challenge rather than automatic byproduct.
Traditional project management assumes status can be gathered through informal check-ins and observation. Remote teams need self-service status systems where any team member can understand project progress, task ownership, and upcoming deadlines without scheduling meetings or sending emails.
Documentation shifts from helpful supplement to critical infrastructure. Decisions, rationale, and context that would normally transfer through conversation must be captured systematically. Remote teams that treat documentation as optional experience constant context reconstruction, slowing progress and frustrating team members.
Trust and Accountability Dynamics
Remote work requires fundamental shifts from time-based to results-based evaluation. Without physical presence indicators, accountability must center on deliverables, milestones, and outcomes rather than hours worked or meetings attended. This transition challenges traditional management approaches built on observation and presence.
Clear deliverable definitions become essential rather than nice-to-have. Ambiguous task descriptions that might get clarified through quick conversations in office settings create significant delays in remote environments. Every task needs explicit success criteria, deadlines, and ownership to prevent coordination failures.
The trust required for remote work extends beyond personal relationships to system confidence. Team members need to trust that important information will be captured and accessible, that their contributions are visible to stakeholders, and that project coordination won't require constant individual effort to maintain visibility.
Tool Complexity Costs
Learning curves amplify dramatically in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events. Tools that seem intuitive during in-person demonstrations often confuse team members working independently. Complex interfaces that office workers might navigate through peer assistance become productivity barriers for remote teams.
Remote workers operate in distraction-rich environments where focus time is precious. Project management tools that require extensive navigation, multiple screens, or complex setup processes interrupt deep work unnecessarily. Simple, visual interfaces become competitive advantages rather than aesthetic preferences.
The cost of tool switching multiplies for remote teams juggling multiple communication platforms, project trackers, and coordination systems. Each additional tool creates cognitive overhead and increases the likelihood of missed information or fragmented communication. This is why choosing simple project management tools becomes crucial for remote team success.
Remote Team Project Management Challenges
Time Zone Coordination Nightmares
Scheduling across multiple time zones transforms simple coordination into complex optimization problems. Finding meeting times that work for team members in California, New York, London, and Mumbai often means someone joins at inconvenient hours or misses critical discussions entirely.
Decision-making delays become project killers when approvals require input from stakeholders across different continents. What should be quick decisions stretch into multi-day processes, creating bottlenecks that cascade through project timelines and frustrate team members waiting for direction.
Follow-the-sun workflows, where projects move continuously across time zones, require sophisticated handoff procedures and documentation standards. Without proper coordination systems, work stops at regional boundaries rather than flowing smoothly around the clock.
Meeting fatigue hits remote teams particularly hard when attempting to accommodate global schedules. The constant compromise of inconvenient meeting times leads to reduced participation, poor decision quality, and team member resentment about work-life balance disruption.

Information Silos and Knowledge Gaps
The tribal knowledge that develops naturally through office interactions—knowing who to ask about specific topics, understanding project history, and awareness of upcoming changes—disappears in remote environments without systematic knowledge management.
Documentation becomes critical infrastructure, but most teams treat it as administrative overhead rather than core productivity tool. Important decisions made in video calls or chat conversations often remain undocumented, creating knowledge gaps for team members who weren't present or joined later.
Onboarding new remote team members requires deliberate knowledge transfer processes that many organizations haven't developed. New hires struggle to understand project context, team dynamics, and informal procedures that office workers absorb through osmosis.
Context sharing for complex projects becomes exponentially more difficult when explanations can't happen through quick screen sharing or whiteboard sketches. Remote teams need project management tools that capture and communicate context visually and accessibly.
Accountability and Progress Tracking
Work visibility challenges make traditional management approaches ineffective for remote teams. Managers can't gauge productivity through observation, requiring new systems for understanding individual and project progress without micromanagement.
Results measurement becomes essential when time tracking loses relevance. Remote teams need clear milestone definitions, deliverable specifications, and success criteria that enable autonomous work while maintaining accountability to team and organizational goals.
Performance evaluation complexities multiply when traditional indicators—meeting participation, office presence, and informal collaboration—no longer apply. Remote team performance must be measured through output quality, deadline adherence, and contribution to team objectives.
Tool Overload and Integration Issues
Multiple communication channels create information fragmentation where important updates get lost in chat streams, email threads, and project platform notifications. Remote teams often struggle to maintain single sources of truth across their technology stack.
Platform switching fatigue reduces productivity when team members must navigate between email, chat apps, project trackers, file storage, and video conferencing tools to complete basic work coordination. Each tool switch interrupts focus and increases cognitive load.

Integration complexity often requires technical knowledge that small remote teams lack. Connecting project management tools with communication platforms, calendar systems, and file storage requires configuration effort that becomes barrier to adoption rather than productivity enhancement.
Cost accumulation from multiple tool subscriptions hits small remote teams particularly hard. What starts as necessary communication tools often grows into expensive software stack that exceeds budget constraints without delivering proportional productivity benefits. This is especially challenging for small teams seeking project management software under $10 per user.
What Remote Teams Actually Need from PM Tools
Visual Clarity and Immediate Understanding
Remote teams require project management tools that communicate status instantly without requiring navigation, interpretation, or additional context. At-a-glance understanding becomes critical when team members work asynchronously across different time zones and can't ask quick clarifying questions.
Visual progress indicators must work across cultural and linguistic differences. Color coding, progress bars, and status symbols communicate more effectively than text descriptions when team members speak different languages or work in varying cultural contexts.
Intuitive information architecture enables self-service updates where team members can find relevant project information without disturbing colleagues or waiting for responses. Clear navigation and logical organization reduce coordination overhead that kills remote productivity.
Task ownership and deadline visibility needs to be immediately apparent to everyone involved. Remote teams can't rely on informal awareness of who's working on what—this information must be explicit and constantly accessible to prevent confusion and duplicated effort.
Async-First Communication Design
Threaded conversations tied to specific tasks and projects preserve context for team members who join discussions later or work in different time zones. Unlike general chat platforms where important information gets buried in conversation streams, task-specific communication maintains relevance and searchability.
Status update automation reduces manual reporting overhead that exhausts remote team members. Tools that capture progress automatically through task completion, milestone achievement, and deadline updates eliminate redundant status meetings and administrative busywork.
Context preservation for decisions made across time zones ensures that rationale, alternatives considered, and implementation details remain accessible long after initial discussions. Remote teams need searchable decision history that enables informed future choices.
Notification intelligence respects time zones and work hours to prevent communication overload while ensuring urgent information reaches relevant team members promptly. Smart filtering and scheduling reduce interruption while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Simple Onboarding for Distributed Teams
Self-service team member addition eliminates administrative bottlenecks when new people join projects. Remote teams need tools that enable immediate productivity without requiring extensive setup procedures or training sessions across time zones.
Intuitive interfaces reduce training requirements to absolute minimum. When quick questions become formal communication events, tools must be self-explanatory enough that team members can become productive independently without extensive guidance.
Template-based project setup creates consistency across team practices while reducing setup time for new initiatives. Standard structures help distributed teams maintain coordination patterns that work across different projects and team compositions.
Mobile accessibility ensures team members can stay connected and productive regardless of location or device availability. Remote work often involves varied work environments where desktop access isn't guaranteed.
Integration with Remote Work Stack
Calendar synchronization connects project deadlines with individual schedules, enabling realistic timeline planning that accounts for team member availability across different time zones and work patterns.
File sharing integration with cloud storage solutions reduces platform switching and ensures project documents remain accessible from within project management context. Seamless connections prevent information silos between storage and coordination systems.
Communication tool connectivity enables project updates to flow into existing team communication channels without requiring separate platform monitoring. Integration reduces tool fragmentation while maintaining notification effectiveness.
Time zone awareness in scheduling and deadline features prevents coordination mistakes that happen when global teams work with tools designed for single-location use. Automatic time zone conversion and scheduling assistance reduce coordination complexity.
Cost Efficiency for Small Remote Teams
Transparent pricing structures help small teams budget effectively without surprise costs from additional features, integrations, or user additions. Remote teams often operate with tight budgets where unexpected expenses create significant problems.
Scalable costs that grow reasonably with team size enable organic growth without requiring major tool transitions as organizations expand. Pricing flexibility supports remote teams through different growth phases.
No hidden integration fees or setup costs prevent budget surprises that small teams can't absorb. Clear, predictable pricing enables confident tool adoption and long-term planning.
Value optimization over feature maximization recognizes that small remote teams need tools that solve core coordination problems effectively rather than comprehensive feature sets they'll never use.

Complex.so: Purpose-Built for Remote Team Reality
Visual-First Remote Collaboration
Complex.so solves remote team coordination through immediate visual understanding that works across time zones, languages, and cultural differences. Project status becomes instantly clear through color-coded organization and progress indicators that eliminate the need for status meetings or lengthy email updates.
The platform's visual task boards communicate project state at a glance, enabling team members to understand priorities, deadlines, and dependencies without navigating complex menus or interpreting text-heavy interfaces. This visual clarity reduces coordination overhead that typically consumes remote team productivity.
Progress tracking happens automatically through visual indicators that update as team members complete tasks and reach milestones. Remote teams can see project advancement in real-time without requiring manual status reports or constant communication about individual progress.
The interface design prioritizes information density that enables comprehensive project understanding from single screen views. Remote team members can assess project status, identify bottlenecks, and understand next steps without switching between multiple views or platforms.
Async Communication Excellence
Task-level commenting preserves conversation context directly within project structure, eliminating the information fragmentation that plagues remote teams using separate communication tools. Discussions remain connected to relevant work, making decision history searchable and accessible.
@mention functionality respects time zones and work schedules, ensuring important communications reach relevant team members without creating notification overload. Smart notification timing reduces interruptions while maintaining coordination effectiveness across global teams.
Automated status updates eliminate redundant reporting that exhausts remote team members. Progress flows naturally through task completion and milestone achievement, providing stakeholders with current information without requiring manual coordination effort.
The platform captures decision rationale and project context automatically as teams work, creating searchable knowledge bases that prevent information loss common in remote environments. This systematic context preservation supports long-term project success and team member onboarding.
5-Minute Remote Onboarding
New team members become productive immediately through intuitive interface design that requires no training sessions across time zones. The platform's self-explanatory structure enables independent adoption without extensive guidance or documentation.
No complex setup procedures delay team member integration into ongoing projects. Simple invitation and immediate access eliminate onboarding friction that often prevents quick team scaling in remote environments.
Mobile applications provide identical functionality to desktop versions, ensuring team members can contribute effectively regardless of location or device availability. Consistent experience across platforms supports flexible work arrangements without productivity compromise.
The Buffer State of Remote Work 2023 report found that 98% of remote workers want to continue working remotely for the rest of their careers, with 36% saying career growth is easier remotely compared to just 14% in 2022.
Small Remote Team Economics
Pricing transparency eliminates budget surprises that small remote teams can't absorb. Clear, predictable costs enable confident adoption and long-term financial planning without fear of unexpected expenses from feature additions or integrations.
The platform replaces multiple tools commonly used by remote teams—task management, communication threading, file organization, and progress reporting—providing economic efficiency through consolidated functionality rather than expensive tool stack accumulation.
Scalable pricing grows reasonably with team expansion, supporting remote organizations through different growth phases without requiring disruptive tool transitions. Economic flexibility enables organic team development without productivity interruption.
No per-integration fees or hidden costs prevent the budget escalation that commonly affects small teams adopting multiple remote work tools. Comprehensive functionality within single subscription supports predictable financial planning.
Global Team Considerations
Time zone aware scheduling and deadline features prevent coordination mistakes common when global teams use tools designed for single-location use. Automatic time zone conversion and intelligent scheduling reduce coordination complexity across distributed teams.
The platform's performance remains consistent across different internet conditions and geographic locations, ensuring reliable access for team members regardless of local infrastructure quality. Global reliability supports truly distributed team collaboration.
Multi-language interface support and cultural communication pattern accommodation enable effective coordination across diverse teams without requiring common language proficiency for tool navigation and basic project coordination.
Notification intelligence respects cultural work patterns and local holiday schedules, ensuring communication effectiveness while maintaining appropriate work-life boundaries across different regions and time zones.
Remote PM Tool Comparison for Small Teams
Complex.so: The Remote-Optimized Choice
Complex.so addresses remote team challenges through design decisions specifically optimized for distributed collaboration. Visual clarity reduces coordination overhead, async-first communication preserves context across time zones, and simple onboarding eliminates training barriers that delay productivity.
The platform's remote advantages stem from recognizing that distributed teams need fundamentally different coordination approaches than office-based groups. Rather than adapting office-designed tools for remote use, Complex.so builds collaboration patterns that leverage remote work strengths while mitigating inherent challenges.
Small remote teams (5-15 people) achieve immediate productivity without extensive configuration, training periods, or integration complexity. The tool works effectively from day one, enabling focus on project outcomes rather than coordination mechanics.
Economic efficiency comes through consolidated functionality that replaces multiple tools commonly required for remote team coordination. Single subscription provides task management, communication threading, progress tracking, and file organization without additional integration costs.
Asana: Feature-Rich but Complex for Remote
Asana provides comprehensive project management features that appeal to larger organizations with dedicated project management resources. Robust reporting, advanced workflow automation, and extensive customization options support complex project requirements and organizational scaling.
Remote challenges emerge through interface complexity that requires extensive training for effective adoption. The learning curve amplifies in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events, delaying productivity and frustrating team members.
While Asana works well for larger remote teams with dedicated project managers who can handle configuration and training responsibilities, small distributed teams often struggle with adoption complexity that exceeds their coordination benefits.
The platform's extensive feature set can overwhelm small teams who need immediate coordination solutions rather than comprehensive project management infrastructure requiring ongoing administration and optimization.
Trello: Simple but Limited for Remote Coordination
Trello's card-based interface provides intuitive visual organization that works well for basic project coordination and simple task tracking. The simplicity appeals to small teams who need immediate adoption without complex setup procedures.
Remote limitations become apparent when projects require advanced coordination features like time tracking, reporting, dependency management, or integrated communication. The platform's simplicity becomes constraint rather than advantage for complex remote project requirements.
Very small teams with straightforward project needs may find Trello sufficient for basic coordination, but growing remote teams typically outgrow the platform's capabilities as project complexity increases and coordination requirements become more sophisticated.
Integration limitations prevent seamless workflow connections with other remote work tools, creating information silos and platform switching overhead that reduces productivity for distributed teams.

Monday.com: Powerful but Overwhelming for Remote Teams
Monday.com provides highly customizable project management infrastructure with advanced features for complex workflow automation, detailed reporting, and extensive integration capabilities appealing to larger organizations with sophisticated project requirements.
Remote challenges include overwhelming complexity that requires extensive setup and ongoing administration. The platform's power becomes liability for small remote teams who need immediate productivity rather than comprehensive configuration projects.
Training overhead amplifies in remote environments where team members must learn complex interfaces independently without immediate peer assistance. The sophisticated feature set often exceeds small team needs while creating adoption barriers.
Cost complexity through numerous add-ons and feature tiers makes budget planning difficult for small remote teams operating with constrained resources and predictable expense requirements.
Slack/Teams + Basic PM: Communication-Heavy Approach
Combining communication platforms with basic project management creates fragmented coordination where project information spreads across chat streams, shared documents, and simple task lists without integrated structure or searchable organization.
Information gets lost in conversation streams where important project updates, decisions, and deadlines become buried in ongoing chat activity. Retrieving project context requires searching through conversation history rather than accessing organized project structure.
The approach fails to provide visual project overview or systematic progress tracking, forcing remote teams to rely on manual status updates and constant communication for coordination rather than self-service information access.
No structured project organization means task dependencies, milestone tracking, and resource allocation remain invisible, preventing strategic project planning and creating coordination chaos for anything beyond simple task lists.
Remote Team PM Implementation Strategy
Phase 1: Tool Selection and Setup (Week 1)
Begin implementation by evaluating project management tools using remote-specific criteria rather than general feature comparisons. Prioritize visual clarity, async communication capabilities, and simple onboarding over comprehensive feature sets that require extensive configuration.
Focus evaluation on tools that work immediately for distributed teams without requiring training sessions across time zones or complex setup procedures. Test core functionality with actual project scenarios rather than demo environments to understand real-world usability.
Set up initial project structure using basic templates that reflect your team's work patterns. Create sample projects that demonstrate typical workflows while establishing naming conventions and organizational standards that support scalable adoption.
Invite team members gradually to test core functionality with pilot projects before full implementation. This phased approach identifies usability issues and adoption barriers while building confidence through successful early experiences.
Phase 2: Team Onboarding and Training (Week 2)
Schedule onboarding sessions that accommodate different time zones without requiring everyone to attend simultaneously. Create recorded training materials that team members can access independently, reducing coordination overhead while ensuring consistent information transfer.
Develop documentation focused on common use cases and frequently asked questions rather than comprehensive feature explanations. Remote team members need quick reference materials for independent problem-solving rather than exhaustive training manuals.
Start implementation with simple projects that demonstrate value without overwhelming team members with advanced features. Success with basic coordination builds confidence for adopting more sophisticated functionality as comfort levels increase.
Establish communication norms around tool usage, notification preferences, and update frequencies. Clear expectations prevent coordination confusion while respecting individual work patterns and time zone constraints.
Phase 3: Workflow Optimization (Weeks 3-4)
Refine notification settings based on team feedback about communication effectiveness versus interruption frequency. Optimize alert timing and filtering to maintain coordination without creating notification overload that disrupts focus time.
Establish async update rhythms that provide stakeholders with progress information without requiring manual reporting overhead. Automate status communication through milestone completion and deadline achievement rather than scheduled status meetings. Learn more about effective team task management approaches for distributed teams.
Create project templates that capture successful coordination patterns for reuse across similar initiatives. Standardized structures reduce setup time while maintaining flexibility for project-specific requirements and team preferences.
Develop documentation standards that capture decision rationale and context for future reference. Systematic knowledge preservation prevents information loss common in remote environments where informal communication doesn't happen naturally.
Phase 4: Advanced Features and Integration (Month 2)
Integrate project management tools with existing remote work technology stack to reduce platform switching and information fragmentation. Connect calendar systems, communication tools, and file storage to create seamless workflow continuity.
Implement advanced reporting that provides stakeholders with project insights without requiring manual data compilation. Automated progress summaries and trend analysis support strategic decision-making while reducing administrative overhead.
Establish productivity metrics that focus on outcomes rather than activity levels. Track milestone achievement, deadline adherence, and deliverable quality rather than time spent or meetings attended to support results-oriented remote work culture.
Research from Stanford's Nicholas Bloom demonstrates that remote work can increase productivity by 13% when properly implemented with structured coordination systems.
Remote Team PM Best Practices
Async-First Communication
Default to asynchronous communication methods that enable thoughtful responses rather than immediate reactions. Reserve synchronous meetings for complex decision-making, creative collaboration, and relationship building rather than routine information sharing.
Use threaded conversations that preserve context and enable team members to join discussions regardless of time zone constraints. Task-specific communication threads maintain relevance while preventing important information from getting lost in general conversation streams.
Establish response time expectations that balance coordination needs with deep work protection. Clear expectations about urgent versus routine communication prevent anxiety while ensuring important information receives appropriate attention across time zones.
Document decisions and rationale systematically rather than relying on meeting notes or chat conversations. Searchable decision history enables informed future choices while providing context for team members who weren't present during initial discussions.
Documentation and Context Sharing
Create searchable project knowledge bases that capture institutional memory and prevent information loss when team members change or projects evolve. Systematic documentation reduces dependency on individual knowledge while supporting long-term project success.
Maintain clear project history that includes decision rationale, alternative options considered, and implementation details. Comprehensive context helps future team members understand project evolution while supporting informed modification and expansion decisions.
Develop information architecture that enables self-service knowledge discovery. Organized, searchable documentation reduces coordination overhead while ensuring team members can find relevant information independently without interrupting colleagues.
Update documentation systematically as projects evolve rather than treating it as one-time activity. Living documentation that reflects current project state provides ongoing value while preventing knowledge decay common in fast-moving remote environments.
Results-Oriented Accountability
Focus performance evaluation on deliverable quality, milestone achievement, and contribution to team objectives rather than activity indicators like meeting attendance or hours worked. Results-based accountability aligns with remote work strengths while supporting autonomous work styles.
Define success criteria explicitly for every task and milestone to eliminate ambiguity that creates coordination problems in remote environments. Clear expectations enable autonomous work while maintaining alignment with project objectives and team standards.
Implement regular but non-overwhelming progress check-ins that focus on obstacle identification and resource needs rather than detailed status reporting. Strategic support conversations add value while avoiding micromanagement that undermines remote work benefits.
According to GitLab's annual remote work report, 84% of employees report feeling more productive in remote and hybrid work models when proper coordination tools and practices are implemented.
Tool Simplicity and Adoption
Choose project management tools that provide immediate value without requiring extensive configuration or training periods. Prioritize intuitive interfaces and self-explanatory functionality over comprehensive feature sets that create adoption barriers.
Avoid tool proliferation that creates context switching overhead and information fragmentation. Consolidate functionality through integrated platforms rather than accumulating specialized tools that complicate workflow and increase cognitive load.
Prioritize visual clarity that communicates project status instantly without requiring navigation or interpretation. At-a-glance understanding reduces coordination overhead while supporting effective async collaboration across time zones and cultural differences.
Test tool adoption with actual team members in realistic work environments rather than relying on demonstration environments or feature lists. Real-world usability often differs significantly from controlled testing scenarios.
Global Team Considerations
Respect cultural communication preferences and work pattern differences when establishing team coordination norms. Flexible approaches that accommodate cultural diversity create inclusive environments while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Plan project timelines that account for different holiday schedules and cultural observances across team locations. Global awareness prevents coordination problems while demonstrating respect for team member cultural commitments.
Use time zone aware tools and scheduling practices that distribute coordination burden fairly rather than consistently favoring particular geographic regions. Equitable coordination builds team cohesion while preventing resentment from unfair schedule accommodations.
Consider language and cultural context when creating documentation and communication standards. Clear, accessible communication reduces misunderstanding while supporting effective collaboration across diverse global teams.
Common Remote PM Mistakes to Avoid
Over-Communication Compensation
Many remote teams attempt to recreate office-level visibility through excessive status meetings and constant check-ins. This over-correction creates meeting fatigue while interrupting the deep work that makes remote environments productive.
Information overload through multiple communication channels often makes coordination less effective rather than more transparent. Teams that maintain separate streams for email, chat, project updates, and meeting notes create fragmentation that reduces rather than improves visibility.
The temptation to replicate in-person communication patterns through video calls and chat conversations often misses opportunities to leverage async communication strengths. Remote teams thrive when they embrace asynchronous coordination rather than fighting against time zone differences.
Status reporting that requires manual effort from team members creates administrative overhead that reduces productivity. Automated progress tracking through task completion and milestone achievement provides better visibility with less effort.

Tool Complexity Underestimation
Choosing feature-rich project management platforms often creates adoption barriers that prevent effective team coordination. Complex interfaces require training investments that small remote teams often can't make, leading to partial adoption and coordination failures. This is why enterprise project management tools often fail small teams.
Underestimating learning curve impact in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events leads to prolonged productivity reduction. Tools that seem intuitive during sales demonstrations often confuse team members working independently.
Integration complexity that requires technical knowledge often prevents small remote teams from connecting their tool stack effectively. Sophisticated connection capabilities become worthless when teams lack resources to implement and maintain integrations.
Feature addiction leads teams to choose tools based on capability lists rather than actual usage requirements. Comprehensive platforms often overwhelm small teams while creating administrative overhead that exceeds coordination benefits.
One-Size-Fits-All Approaches
Applying in-office project management practices to remote teams ignores fundamental differences in communication patterns, coordination requirements, and work styles. Remote teams need strategies designed for distributed collaboration rather than adapted office approaches.
Assuming global teams can accommodate single time zone scheduling creates unfair burden distribution and reduces participation from team members in inconvenient time zones. Successful remote coordination requires flexible approaches that distribute inconvenience equitably.
Using communication tools designed for co-located teams often creates information fragmentation and reduces async collaboration effectiveness. Remote-optimized tools provide better coordination outcomes than general-purpose communication platforms.
Ignoring cultural communication preferences and work pattern differences creates coordination friction that reduces team effectiveness. Global teams need flexible coordination approaches that accommodate cultural diversity while maintaining project alignment.
Neglecting Onboarding for Remote Context
Insufficient documentation for self-service learning creates dependency on individual knowledge that becomes coordination bottleneck when team members are unavailable across time zones. Remote teams need comprehensive, searchable knowledge bases for independent problem-solving.
Assuming new team members can ask questions easily ignores the communication overhead that makes simple clarifications into formal events in remote environments. Thorough onboarding materials reduce coordination burden while accelerating productivity.
Failing to provide project context and decision history leaves new team members without institutional knowledge that office workers acquire through informal observation and conversation. Systematic context sharing supports effective remote team integration.
Inadequate tool training that assumes intuitive adoption often leads to partial usage and coordination problems. Remote team members need self-paced training materials and clear usage examples for effective tool adoption without time zone coordination requirements.
FAQ Section
How do you maintain accountability with remote teams?
Accountability in remote teams comes through clear deliverable definitions, milestone-based progress tracking, and results-oriented evaluation rather than activity monitoring. Focus on output quality and deadline adherence rather than hours worked or meeting participation.
Establish explicit success criteria for every task and project milestone to eliminate ambiguity that creates coordination problems. Regular but non-overwhelming check-ins should focus on obstacle identification and resource needs rather than detailed status reporting.
Use project management tools that provide visibility into progress and contribution without requiring manual reporting overhead. Automated status updates through task completion and milestone achievement maintain accountability while respecting autonomous work styles.
Document decisions and maintain project history to create accountability through transparency rather than surveillance. Searchable records of contributions and decisions support fair evaluation while building institutional knowledge.
What's the best way to handle time zone differences in project management?
Time zone coordination requires tools and practices designed for asynchronous collaboration rather than attempting to find universal meeting times. Prioritize async communication methods that enable thoughtful participation regardless of local time constraints.
Use project management platforms with time zone awareness that automatically convert deadlines and scheduling information for individual team members. Avoid coordination mistakes through tools that handle time zone complexity automatically.
Establish follow-the-sun workflows where projects move continuously across time zones with proper handoff procedures and documentation standards. Create systematic knowledge transfer processes that enable work continuity without requiring overlap hours.
Distribute coordination burden equitably rather than consistently favoring particular geographic regions. Rotate meeting times and deadline accommodations to prevent unfair schedule impact on specific team members.
How do you onboard new team members to PM tools remotely?
Remote onboarding requires comprehensive self-service materials that enable independent learning without real-time guidance across time zones. Create recorded training sessions, documentation, and usage examples that new team members can access at convenient times.
Start with simple projects that demonstrate core functionality before introducing advanced features. Success with basic coordination builds confidence while preventing overwhelming complexity during initial adoption period.
Provide project templates and usage examples that reflect actual work patterns rather than theoretical scenarios. Real-world context helps new team members understand tool application to their specific responsibilities and project requirements.
Assign onboarding buddies in compatible time zones who can provide guidance and answer questions without requiring coordination across inconvenient hours. Peer support accelerates adoption while building team relationships.
Should remote teams use different tools than in-office teams?
Remote teams benefit from tools specifically designed for distributed collaboration rather than adapted office-based solutions. Visual clarity, async communication capabilities, and simple onboarding become critical factors that aren't as important for co-located teams. Consider exploring no-code project management solutions for easier adoption.
Prioritize platforms that provide at-a-glance project understanding and self-service information access. Remote teams can't rely on informal awareness and quick questions that happen naturally in shared physical spaces.
Choose tools with mobile optimization and reliable performance across different internet conditions since remote team members work in varied environments with different technology constraints.
Consider economic efficiency more carefully since remote teams often operate with distributed budget authority and need predictable costs rather than enterprise pricing structures designed for centralized purchasing decisions.
How do you prevent remote team communication overload?
Communication overload prevention requires strategic tool selection that consolidates information streams rather than fragmenting coordination across multiple platforms. Choose integrated solutions that provide project coordination within single interface.
Establish notification intelligence that respects time zones and work schedules while ensuring urgent information reaches relevant team members promptly. Smart filtering reduces interruption while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Default to async communication methods that enable thoughtful responses rather than immediate reactions. Reserve synchronous meetings for complex decision-making and creative collaboration rather than routine information sharing.
Create clear communication norms around urgency levels, response time expectations, and appropriate channels for different types of information. Explicit guidelines prevent anxiety while ensuring important coordination doesn't get lost in routine updates.
Ready to streamline your remote team's project management? Try Complex.so free for 14 days and discover how visual-first coordination transforms distributed team productivity. No credit card required, no complex setup—just immediate organization that works across time zones.
Looking for more remote team strategies? Explore our complete guide to small team collaboration tools, discover 5 project management tips specifically for small teams, and learn about building high-performing remote teams. For teams just getting started, check out our 5-minute setup guide.
Remote teams don't fail because of distance—they fail because of coordination chaos.
The shift to distributed work has exposed a fundamental truth: traditional project management approaches crumble when teams spread across time zones. While 58% of the American workforce now has access to remote work options, most organizations still rely on project management strategies designed for conference rooms and cubicles.
This disconnect creates real coordination challenges. While recent Project Management Institute research shows remote teams achieve similar success rates to in-person teams (73.2% vs 74.6%), they face unique obstacles including communication overhead and visibility gaps that require different management approaches. The tools that worked for in-person collaboration—impromptu desk visits, whiteboard sessions, and hallway conversations—simply don't translate to distributed environments.
Remote work has evolved from emergency pandemic response to strategic business choice. Companies embracing distributed teams access global talent pools, reduce overhead costs, and offer flexibility that attracts top performers. However, success requires fundamentally different project management approaches.
Remote team project management isn't about replicating office dynamics through video calls and chat apps. It's about building systems that thrive on asynchronous communication, visual clarity, and results-oriented accountability. The teams that master these principles don't just survive remote work—they outperform their office-bound competitors.
The stakes are high. Organizations that nail remote project management gain competitive advantages: faster hiring, lower costs, and access to global expertise. Those that don't face constant firefighting, missed deadlines, and team member burnout from coordination overhead.
This guide reveals the tools and strategies that actually work for distributed teams. You'll discover why remote teams need different approaches, what separates successful remote project management from office-based coordination, and how to implement systems that deliver results regardless of where your team members work.
According to McKinsey research, 58% of the American workforce now has access to remote work options, representing about 92 million workers with flexible work capability.
Why Remote Teams Need Different Project Management
Communication Overhead Multiplication
Remote work transforms simple conversations into complex coordination challenges. What takes thirty seconds at someone's desk becomes email threads, delayed responses, and decision bottlenecks. Microsoft Teams data shows a 200% increase in meeting minutes during the initial remote work transition, highlighting how teams struggle to recreate informal information flow in distributed environments.
Time zone differences amplify these challenges exponentially. A decision that requires input from team members in New York, London, and Singapore can take 24-48 hours instead of 24 minutes. This delay cascades through project timelines, creating compounding coordination costs that office-based teams never experience.
The loss of peripheral awareness—knowing what others are working on through visual and auditory cues—forces remote teams to create explicit communication systems. Without deliberate coordination structures, information silos develop quickly, leading to duplicated work, missed dependencies, and strategic misalignment.

Visibility and Transparency Requirements
In physical offices, project status lives in observable behaviors: busy team members, progress on whiteboards, and informal updates during coffee breaks. Remote environments eliminate these ambient status indicators, making project visibility an intentional design challenge rather than automatic byproduct.
Traditional project management assumes status can be gathered through informal check-ins and observation. Remote teams need self-service status systems where any team member can understand project progress, task ownership, and upcoming deadlines without scheduling meetings or sending emails.
Documentation shifts from helpful supplement to critical infrastructure. Decisions, rationale, and context that would normally transfer through conversation must be captured systematically. Remote teams that treat documentation as optional experience constant context reconstruction, slowing progress and frustrating team members.
Trust and Accountability Dynamics
Remote work requires fundamental shifts from time-based to results-based evaluation. Without physical presence indicators, accountability must center on deliverables, milestones, and outcomes rather than hours worked or meetings attended. This transition challenges traditional management approaches built on observation and presence.
Clear deliverable definitions become essential rather than nice-to-have. Ambiguous task descriptions that might get clarified through quick conversations in office settings create significant delays in remote environments. Every task needs explicit success criteria, deadlines, and ownership to prevent coordination failures.
The trust required for remote work extends beyond personal relationships to system confidence. Team members need to trust that important information will be captured and accessible, that their contributions are visible to stakeholders, and that project coordination won't require constant individual effort to maintain visibility.
Tool Complexity Costs
Learning curves amplify dramatically in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events. Tools that seem intuitive during in-person demonstrations often confuse team members working independently. Complex interfaces that office workers might navigate through peer assistance become productivity barriers for remote teams.
Remote workers operate in distraction-rich environments where focus time is precious. Project management tools that require extensive navigation, multiple screens, or complex setup processes interrupt deep work unnecessarily. Simple, visual interfaces become competitive advantages rather than aesthetic preferences.
The cost of tool switching multiplies for remote teams juggling multiple communication platforms, project trackers, and coordination systems. Each additional tool creates cognitive overhead and increases the likelihood of missed information or fragmented communication. This is why choosing simple project management tools becomes crucial for remote team success.
Remote Team Project Management Challenges
Time Zone Coordination Nightmares
Scheduling across multiple time zones transforms simple coordination into complex optimization problems. Finding meeting times that work for team members in California, New York, London, and Mumbai often means someone joins at inconvenient hours or misses critical discussions entirely.
Decision-making delays become project killers when approvals require input from stakeholders across different continents. What should be quick decisions stretch into multi-day processes, creating bottlenecks that cascade through project timelines and frustrate team members waiting for direction.
Follow-the-sun workflows, where projects move continuously across time zones, require sophisticated handoff procedures and documentation standards. Without proper coordination systems, work stops at regional boundaries rather than flowing smoothly around the clock.
Meeting fatigue hits remote teams particularly hard when attempting to accommodate global schedules. The constant compromise of inconvenient meeting times leads to reduced participation, poor decision quality, and team member resentment about work-life balance disruption.

Information Silos and Knowledge Gaps
The tribal knowledge that develops naturally through office interactions—knowing who to ask about specific topics, understanding project history, and awareness of upcoming changes—disappears in remote environments without systematic knowledge management.
Documentation becomes critical infrastructure, but most teams treat it as administrative overhead rather than core productivity tool. Important decisions made in video calls or chat conversations often remain undocumented, creating knowledge gaps for team members who weren't present or joined later.
Onboarding new remote team members requires deliberate knowledge transfer processes that many organizations haven't developed. New hires struggle to understand project context, team dynamics, and informal procedures that office workers absorb through osmosis.
Context sharing for complex projects becomes exponentially more difficult when explanations can't happen through quick screen sharing or whiteboard sketches. Remote teams need project management tools that capture and communicate context visually and accessibly.
Accountability and Progress Tracking
Work visibility challenges make traditional management approaches ineffective for remote teams. Managers can't gauge productivity through observation, requiring new systems for understanding individual and project progress without micromanagement.
Results measurement becomes essential when time tracking loses relevance. Remote teams need clear milestone definitions, deliverable specifications, and success criteria that enable autonomous work while maintaining accountability to team and organizational goals.
Performance evaluation complexities multiply when traditional indicators—meeting participation, office presence, and informal collaboration—no longer apply. Remote team performance must be measured through output quality, deadline adherence, and contribution to team objectives.
Tool Overload and Integration Issues
Multiple communication channels create information fragmentation where important updates get lost in chat streams, email threads, and project platform notifications. Remote teams often struggle to maintain single sources of truth across their technology stack.
Platform switching fatigue reduces productivity when team members must navigate between email, chat apps, project trackers, file storage, and video conferencing tools to complete basic work coordination. Each tool switch interrupts focus and increases cognitive load.

Integration complexity often requires technical knowledge that small remote teams lack. Connecting project management tools with communication platforms, calendar systems, and file storage requires configuration effort that becomes barrier to adoption rather than productivity enhancement.
Cost accumulation from multiple tool subscriptions hits small remote teams particularly hard. What starts as necessary communication tools often grows into expensive software stack that exceeds budget constraints without delivering proportional productivity benefits. This is especially challenging for small teams seeking project management software under $10 per user.
What Remote Teams Actually Need from PM Tools
Visual Clarity and Immediate Understanding
Remote teams require project management tools that communicate status instantly without requiring navigation, interpretation, or additional context. At-a-glance understanding becomes critical when team members work asynchronously across different time zones and can't ask quick clarifying questions.
Visual progress indicators must work across cultural and linguistic differences. Color coding, progress bars, and status symbols communicate more effectively than text descriptions when team members speak different languages or work in varying cultural contexts.
Intuitive information architecture enables self-service updates where team members can find relevant project information without disturbing colleagues or waiting for responses. Clear navigation and logical organization reduce coordination overhead that kills remote productivity.
Task ownership and deadline visibility needs to be immediately apparent to everyone involved. Remote teams can't rely on informal awareness of who's working on what—this information must be explicit and constantly accessible to prevent confusion and duplicated effort.
Async-First Communication Design
Threaded conversations tied to specific tasks and projects preserve context for team members who join discussions later or work in different time zones. Unlike general chat platforms where important information gets buried in conversation streams, task-specific communication maintains relevance and searchability.
Status update automation reduces manual reporting overhead that exhausts remote team members. Tools that capture progress automatically through task completion, milestone achievement, and deadline updates eliminate redundant status meetings and administrative busywork.
Context preservation for decisions made across time zones ensures that rationale, alternatives considered, and implementation details remain accessible long after initial discussions. Remote teams need searchable decision history that enables informed future choices.
Notification intelligence respects time zones and work hours to prevent communication overload while ensuring urgent information reaches relevant team members promptly. Smart filtering and scheduling reduce interruption while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Simple Onboarding for Distributed Teams
Self-service team member addition eliminates administrative bottlenecks when new people join projects. Remote teams need tools that enable immediate productivity without requiring extensive setup procedures or training sessions across time zones.
Intuitive interfaces reduce training requirements to absolute minimum. When quick questions become formal communication events, tools must be self-explanatory enough that team members can become productive independently without extensive guidance.
Template-based project setup creates consistency across team practices while reducing setup time for new initiatives. Standard structures help distributed teams maintain coordination patterns that work across different projects and team compositions.
Mobile accessibility ensures team members can stay connected and productive regardless of location or device availability. Remote work often involves varied work environments where desktop access isn't guaranteed.
Integration with Remote Work Stack
Calendar synchronization connects project deadlines with individual schedules, enabling realistic timeline planning that accounts for team member availability across different time zones and work patterns.
File sharing integration with cloud storage solutions reduces platform switching and ensures project documents remain accessible from within project management context. Seamless connections prevent information silos between storage and coordination systems.
Communication tool connectivity enables project updates to flow into existing team communication channels without requiring separate platform monitoring. Integration reduces tool fragmentation while maintaining notification effectiveness.
Time zone awareness in scheduling and deadline features prevents coordination mistakes that happen when global teams work with tools designed for single-location use. Automatic time zone conversion and scheduling assistance reduce coordination complexity.
Cost Efficiency for Small Remote Teams
Transparent pricing structures help small teams budget effectively without surprise costs from additional features, integrations, or user additions. Remote teams often operate with tight budgets where unexpected expenses create significant problems.
Scalable costs that grow reasonably with team size enable organic growth without requiring major tool transitions as organizations expand. Pricing flexibility supports remote teams through different growth phases.
No hidden integration fees or setup costs prevent budget surprises that small teams can't absorb. Clear, predictable pricing enables confident tool adoption and long-term planning.
Value optimization over feature maximization recognizes that small remote teams need tools that solve core coordination problems effectively rather than comprehensive feature sets they'll never use.

Complex.so: Purpose-Built for Remote Team Reality
Visual-First Remote Collaboration
Complex.so solves remote team coordination through immediate visual understanding that works across time zones, languages, and cultural differences. Project status becomes instantly clear through color-coded organization and progress indicators that eliminate the need for status meetings or lengthy email updates.
The platform's visual task boards communicate project state at a glance, enabling team members to understand priorities, deadlines, and dependencies without navigating complex menus or interpreting text-heavy interfaces. This visual clarity reduces coordination overhead that typically consumes remote team productivity.
Progress tracking happens automatically through visual indicators that update as team members complete tasks and reach milestones. Remote teams can see project advancement in real-time without requiring manual status reports or constant communication about individual progress.
The interface design prioritizes information density that enables comprehensive project understanding from single screen views. Remote team members can assess project status, identify bottlenecks, and understand next steps without switching between multiple views or platforms.
Async Communication Excellence
Task-level commenting preserves conversation context directly within project structure, eliminating the information fragmentation that plagues remote teams using separate communication tools. Discussions remain connected to relevant work, making decision history searchable and accessible.
@mention functionality respects time zones and work schedules, ensuring important communications reach relevant team members without creating notification overload. Smart notification timing reduces interruptions while maintaining coordination effectiveness across global teams.
Automated status updates eliminate redundant reporting that exhausts remote team members. Progress flows naturally through task completion and milestone achievement, providing stakeholders with current information without requiring manual coordination effort.
The platform captures decision rationale and project context automatically as teams work, creating searchable knowledge bases that prevent information loss common in remote environments. This systematic context preservation supports long-term project success and team member onboarding.
5-Minute Remote Onboarding
New team members become productive immediately through intuitive interface design that requires no training sessions across time zones. The platform's self-explanatory structure enables independent adoption without extensive guidance or documentation.
No complex setup procedures delay team member integration into ongoing projects. Simple invitation and immediate access eliminate onboarding friction that often prevents quick team scaling in remote environments.
Mobile applications provide identical functionality to desktop versions, ensuring team members can contribute effectively regardless of location or device availability. Consistent experience across platforms supports flexible work arrangements without productivity compromise.
The Buffer State of Remote Work 2023 report found that 98% of remote workers want to continue working remotely for the rest of their careers, with 36% saying career growth is easier remotely compared to just 14% in 2022.
Small Remote Team Economics
Pricing transparency eliminates budget surprises that small remote teams can't absorb. Clear, predictable costs enable confident adoption and long-term financial planning without fear of unexpected expenses from feature additions or integrations.
The platform replaces multiple tools commonly used by remote teams—task management, communication threading, file organization, and progress reporting—providing economic efficiency through consolidated functionality rather than expensive tool stack accumulation.
Scalable pricing grows reasonably with team expansion, supporting remote organizations through different growth phases without requiring disruptive tool transitions. Economic flexibility enables organic team development without productivity interruption.
No per-integration fees or hidden costs prevent the budget escalation that commonly affects small teams adopting multiple remote work tools. Comprehensive functionality within single subscription supports predictable financial planning.
Global Team Considerations
Time zone aware scheduling and deadline features prevent coordination mistakes common when global teams use tools designed for single-location use. Automatic time zone conversion and intelligent scheduling reduce coordination complexity across distributed teams.
The platform's performance remains consistent across different internet conditions and geographic locations, ensuring reliable access for team members regardless of local infrastructure quality. Global reliability supports truly distributed team collaboration.
Multi-language interface support and cultural communication pattern accommodation enable effective coordination across diverse teams without requiring common language proficiency for tool navigation and basic project coordination.
Notification intelligence respects cultural work patterns and local holiday schedules, ensuring communication effectiveness while maintaining appropriate work-life boundaries across different regions and time zones.
Remote PM Tool Comparison for Small Teams
Complex.so: The Remote-Optimized Choice
Complex.so addresses remote team challenges through design decisions specifically optimized for distributed collaboration. Visual clarity reduces coordination overhead, async-first communication preserves context across time zones, and simple onboarding eliminates training barriers that delay productivity.
The platform's remote advantages stem from recognizing that distributed teams need fundamentally different coordination approaches than office-based groups. Rather than adapting office-designed tools for remote use, Complex.so builds collaboration patterns that leverage remote work strengths while mitigating inherent challenges.
Small remote teams (5-15 people) achieve immediate productivity without extensive configuration, training periods, or integration complexity. The tool works effectively from day one, enabling focus on project outcomes rather than coordination mechanics.
Economic efficiency comes through consolidated functionality that replaces multiple tools commonly required for remote team coordination. Single subscription provides task management, communication threading, progress tracking, and file organization without additional integration costs.
Asana: Feature-Rich but Complex for Remote
Asana provides comprehensive project management features that appeal to larger organizations with dedicated project management resources. Robust reporting, advanced workflow automation, and extensive customization options support complex project requirements and organizational scaling.
Remote challenges emerge through interface complexity that requires extensive training for effective adoption. The learning curve amplifies in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events, delaying productivity and frustrating team members.
While Asana works well for larger remote teams with dedicated project managers who can handle configuration and training responsibilities, small distributed teams often struggle with adoption complexity that exceeds their coordination benefits.
The platform's extensive feature set can overwhelm small teams who need immediate coordination solutions rather than comprehensive project management infrastructure requiring ongoing administration and optimization.
Trello: Simple but Limited for Remote Coordination
Trello's card-based interface provides intuitive visual organization that works well for basic project coordination and simple task tracking. The simplicity appeals to small teams who need immediate adoption without complex setup procedures.
Remote limitations become apparent when projects require advanced coordination features like time tracking, reporting, dependency management, or integrated communication. The platform's simplicity becomes constraint rather than advantage for complex remote project requirements.
Very small teams with straightforward project needs may find Trello sufficient for basic coordination, but growing remote teams typically outgrow the platform's capabilities as project complexity increases and coordination requirements become more sophisticated.
Integration limitations prevent seamless workflow connections with other remote work tools, creating information silos and platform switching overhead that reduces productivity for distributed teams.

Monday.com: Powerful but Overwhelming for Remote Teams
Monday.com provides highly customizable project management infrastructure with advanced features for complex workflow automation, detailed reporting, and extensive integration capabilities appealing to larger organizations with sophisticated project requirements.
Remote challenges include overwhelming complexity that requires extensive setup and ongoing administration. The platform's power becomes liability for small remote teams who need immediate productivity rather than comprehensive configuration projects.
Training overhead amplifies in remote environments where team members must learn complex interfaces independently without immediate peer assistance. The sophisticated feature set often exceeds small team needs while creating adoption barriers.
Cost complexity through numerous add-ons and feature tiers makes budget planning difficult for small remote teams operating with constrained resources and predictable expense requirements.
Slack/Teams + Basic PM: Communication-Heavy Approach
Combining communication platforms with basic project management creates fragmented coordination where project information spreads across chat streams, shared documents, and simple task lists without integrated structure or searchable organization.
Information gets lost in conversation streams where important project updates, decisions, and deadlines become buried in ongoing chat activity. Retrieving project context requires searching through conversation history rather than accessing organized project structure.
The approach fails to provide visual project overview or systematic progress tracking, forcing remote teams to rely on manual status updates and constant communication for coordination rather than self-service information access.
No structured project organization means task dependencies, milestone tracking, and resource allocation remain invisible, preventing strategic project planning and creating coordination chaos for anything beyond simple task lists.
Remote Team PM Implementation Strategy
Phase 1: Tool Selection and Setup (Week 1)
Begin implementation by evaluating project management tools using remote-specific criteria rather than general feature comparisons. Prioritize visual clarity, async communication capabilities, and simple onboarding over comprehensive feature sets that require extensive configuration.
Focus evaluation on tools that work immediately for distributed teams without requiring training sessions across time zones or complex setup procedures. Test core functionality with actual project scenarios rather than demo environments to understand real-world usability.
Set up initial project structure using basic templates that reflect your team's work patterns. Create sample projects that demonstrate typical workflows while establishing naming conventions and organizational standards that support scalable adoption.
Invite team members gradually to test core functionality with pilot projects before full implementation. This phased approach identifies usability issues and adoption barriers while building confidence through successful early experiences.
Phase 2: Team Onboarding and Training (Week 2)
Schedule onboarding sessions that accommodate different time zones without requiring everyone to attend simultaneously. Create recorded training materials that team members can access independently, reducing coordination overhead while ensuring consistent information transfer.
Develop documentation focused on common use cases and frequently asked questions rather than comprehensive feature explanations. Remote team members need quick reference materials for independent problem-solving rather than exhaustive training manuals.
Start implementation with simple projects that demonstrate value without overwhelming team members with advanced features. Success with basic coordination builds confidence for adopting more sophisticated functionality as comfort levels increase.
Establish communication norms around tool usage, notification preferences, and update frequencies. Clear expectations prevent coordination confusion while respecting individual work patterns and time zone constraints.
Phase 3: Workflow Optimization (Weeks 3-4)
Refine notification settings based on team feedback about communication effectiveness versus interruption frequency. Optimize alert timing and filtering to maintain coordination without creating notification overload that disrupts focus time.
Establish async update rhythms that provide stakeholders with progress information without requiring manual reporting overhead. Automate status communication through milestone completion and deadline achievement rather than scheduled status meetings. Learn more about effective team task management approaches for distributed teams.
Create project templates that capture successful coordination patterns for reuse across similar initiatives. Standardized structures reduce setup time while maintaining flexibility for project-specific requirements and team preferences.
Develop documentation standards that capture decision rationale and context for future reference. Systematic knowledge preservation prevents information loss common in remote environments where informal communication doesn't happen naturally.
Phase 4: Advanced Features and Integration (Month 2)
Integrate project management tools with existing remote work technology stack to reduce platform switching and information fragmentation. Connect calendar systems, communication tools, and file storage to create seamless workflow continuity.
Implement advanced reporting that provides stakeholders with project insights without requiring manual data compilation. Automated progress summaries and trend analysis support strategic decision-making while reducing administrative overhead.
Establish productivity metrics that focus on outcomes rather than activity levels. Track milestone achievement, deadline adherence, and deliverable quality rather than time spent or meetings attended to support results-oriented remote work culture.
Research from Stanford's Nicholas Bloom demonstrates that remote work can increase productivity by 13% when properly implemented with structured coordination systems.
Remote Team PM Best Practices
Async-First Communication
Default to asynchronous communication methods that enable thoughtful responses rather than immediate reactions. Reserve synchronous meetings for complex decision-making, creative collaboration, and relationship building rather than routine information sharing.
Use threaded conversations that preserve context and enable team members to join discussions regardless of time zone constraints. Task-specific communication threads maintain relevance while preventing important information from getting lost in general conversation streams.
Establish response time expectations that balance coordination needs with deep work protection. Clear expectations about urgent versus routine communication prevent anxiety while ensuring important information receives appropriate attention across time zones.
Document decisions and rationale systematically rather than relying on meeting notes or chat conversations. Searchable decision history enables informed future choices while providing context for team members who weren't present during initial discussions.
Documentation and Context Sharing
Create searchable project knowledge bases that capture institutional memory and prevent information loss when team members change or projects evolve. Systematic documentation reduces dependency on individual knowledge while supporting long-term project success.
Maintain clear project history that includes decision rationale, alternative options considered, and implementation details. Comprehensive context helps future team members understand project evolution while supporting informed modification and expansion decisions.
Develop information architecture that enables self-service knowledge discovery. Organized, searchable documentation reduces coordination overhead while ensuring team members can find relevant information independently without interrupting colleagues.
Update documentation systematically as projects evolve rather than treating it as one-time activity. Living documentation that reflects current project state provides ongoing value while preventing knowledge decay common in fast-moving remote environments.
Results-Oriented Accountability
Focus performance evaluation on deliverable quality, milestone achievement, and contribution to team objectives rather than activity indicators like meeting attendance or hours worked. Results-based accountability aligns with remote work strengths while supporting autonomous work styles.
Define success criteria explicitly for every task and milestone to eliminate ambiguity that creates coordination problems in remote environments. Clear expectations enable autonomous work while maintaining alignment with project objectives and team standards.
Implement regular but non-overwhelming progress check-ins that focus on obstacle identification and resource needs rather than detailed status reporting. Strategic support conversations add value while avoiding micromanagement that undermines remote work benefits.
According to GitLab's annual remote work report, 84% of employees report feeling more productive in remote and hybrid work models when proper coordination tools and practices are implemented.
Tool Simplicity and Adoption
Choose project management tools that provide immediate value without requiring extensive configuration or training periods. Prioritize intuitive interfaces and self-explanatory functionality over comprehensive feature sets that create adoption barriers.
Avoid tool proliferation that creates context switching overhead and information fragmentation. Consolidate functionality through integrated platforms rather than accumulating specialized tools that complicate workflow and increase cognitive load.
Prioritize visual clarity that communicates project status instantly without requiring navigation or interpretation. At-a-glance understanding reduces coordination overhead while supporting effective async collaboration across time zones and cultural differences.
Test tool adoption with actual team members in realistic work environments rather than relying on demonstration environments or feature lists. Real-world usability often differs significantly from controlled testing scenarios.
Global Team Considerations
Respect cultural communication preferences and work pattern differences when establishing team coordination norms. Flexible approaches that accommodate cultural diversity create inclusive environments while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Plan project timelines that account for different holiday schedules and cultural observances across team locations. Global awareness prevents coordination problems while demonstrating respect for team member cultural commitments.
Use time zone aware tools and scheduling practices that distribute coordination burden fairly rather than consistently favoring particular geographic regions. Equitable coordination builds team cohesion while preventing resentment from unfair schedule accommodations.
Consider language and cultural context when creating documentation and communication standards. Clear, accessible communication reduces misunderstanding while supporting effective collaboration across diverse global teams.
Common Remote PM Mistakes to Avoid
Over-Communication Compensation
Many remote teams attempt to recreate office-level visibility through excessive status meetings and constant check-ins. This over-correction creates meeting fatigue while interrupting the deep work that makes remote environments productive.
Information overload through multiple communication channels often makes coordination less effective rather than more transparent. Teams that maintain separate streams for email, chat, project updates, and meeting notes create fragmentation that reduces rather than improves visibility.
The temptation to replicate in-person communication patterns through video calls and chat conversations often misses opportunities to leverage async communication strengths. Remote teams thrive when they embrace asynchronous coordination rather than fighting against time zone differences.
Status reporting that requires manual effort from team members creates administrative overhead that reduces productivity. Automated progress tracking through task completion and milestone achievement provides better visibility with less effort.

Tool Complexity Underestimation
Choosing feature-rich project management platforms often creates adoption barriers that prevent effective team coordination. Complex interfaces require training investments that small remote teams often can't make, leading to partial adoption and coordination failures. This is why enterprise project management tools often fail small teams.
Underestimating learning curve impact in remote environments where quick questions become formal communication events leads to prolonged productivity reduction. Tools that seem intuitive during sales demonstrations often confuse team members working independently.
Integration complexity that requires technical knowledge often prevents small remote teams from connecting their tool stack effectively. Sophisticated connection capabilities become worthless when teams lack resources to implement and maintain integrations.
Feature addiction leads teams to choose tools based on capability lists rather than actual usage requirements. Comprehensive platforms often overwhelm small teams while creating administrative overhead that exceeds coordination benefits.
One-Size-Fits-All Approaches
Applying in-office project management practices to remote teams ignores fundamental differences in communication patterns, coordination requirements, and work styles. Remote teams need strategies designed for distributed collaboration rather than adapted office approaches.
Assuming global teams can accommodate single time zone scheduling creates unfair burden distribution and reduces participation from team members in inconvenient time zones. Successful remote coordination requires flexible approaches that distribute inconvenience equitably.
Using communication tools designed for co-located teams often creates information fragmentation and reduces async collaboration effectiveness. Remote-optimized tools provide better coordination outcomes than general-purpose communication platforms.
Ignoring cultural communication preferences and work pattern differences creates coordination friction that reduces team effectiveness. Global teams need flexible coordination approaches that accommodate cultural diversity while maintaining project alignment.
Neglecting Onboarding for Remote Context
Insufficient documentation for self-service learning creates dependency on individual knowledge that becomes coordination bottleneck when team members are unavailable across time zones. Remote teams need comprehensive, searchable knowledge bases for independent problem-solving.
Assuming new team members can ask questions easily ignores the communication overhead that makes simple clarifications into formal events in remote environments. Thorough onboarding materials reduce coordination burden while accelerating productivity.
Failing to provide project context and decision history leaves new team members without institutional knowledge that office workers acquire through informal observation and conversation. Systematic context sharing supports effective remote team integration.
Inadequate tool training that assumes intuitive adoption often leads to partial usage and coordination problems. Remote team members need self-paced training materials and clear usage examples for effective tool adoption without time zone coordination requirements.
FAQ Section
How do you maintain accountability with remote teams?
Accountability in remote teams comes through clear deliverable definitions, milestone-based progress tracking, and results-oriented evaluation rather than activity monitoring. Focus on output quality and deadline adherence rather than hours worked or meeting participation.
Establish explicit success criteria for every task and project milestone to eliminate ambiguity that creates coordination problems. Regular but non-overwhelming check-ins should focus on obstacle identification and resource needs rather than detailed status reporting.
Use project management tools that provide visibility into progress and contribution without requiring manual reporting overhead. Automated status updates through task completion and milestone achievement maintain accountability while respecting autonomous work styles.
Document decisions and maintain project history to create accountability through transparency rather than surveillance. Searchable records of contributions and decisions support fair evaluation while building institutional knowledge.
What's the best way to handle time zone differences in project management?
Time zone coordination requires tools and practices designed for asynchronous collaboration rather than attempting to find universal meeting times. Prioritize async communication methods that enable thoughtful participation regardless of local time constraints.
Use project management platforms with time zone awareness that automatically convert deadlines and scheduling information for individual team members. Avoid coordination mistakes through tools that handle time zone complexity automatically.
Establish follow-the-sun workflows where projects move continuously across time zones with proper handoff procedures and documentation standards. Create systematic knowledge transfer processes that enable work continuity without requiring overlap hours.
Distribute coordination burden equitably rather than consistently favoring particular geographic regions. Rotate meeting times and deadline accommodations to prevent unfair schedule impact on specific team members.
How do you onboard new team members to PM tools remotely?
Remote onboarding requires comprehensive self-service materials that enable independent learning without real-time guidance across time zones. Create recorded training sessions, documentation, and usage examples that new team members can access at convenient times.
Start with simple projects that demonstrate core functionality before introducing advanced features. Success with basic coordination builds confidence while preventing overwhelming complexity during initial adoption period.
Provide project templates and usage examples that reflect actual work patterns rather than theoretical scenarios. Real-world context helps new team members understand tool application to their specific responsibilities and project requirements.
Assign onboarding buddies in compatible time zones who can provide guidance and answer questions without requiring coordination across inconvenient hours. Peer support accelerates adoption while building team relationships.
Should remote teams use different tools than in-office teams?
Remote teams benefit from tools specifically designed for distributed collaboration rather than adapted office-based solutions. Visual clarity, async communication capabilities, and simple onboarding become critical factors that aren't as important for co-located teams. Consider exploring no-code project management solutions for easier adoption.
Prioritize platforms that provide at-a-glance project understanding and self-service information access. Remote teams can't rely on informal awareness and quick questions that happen naturally in shared physical spaces.
Choose tools with mobile optimization and reliable performance across different internet conditions since remote team members work in varied environments with different technology constraints.
Consider economic efficiency more carefully since remote teams often operate with distributed budget authority and need predictable costs rather than enterprise pricing structures designed for centralized purchasing decisions.
How do you prevent remote team communication overload?
Communication overload prevention requires strategic tool selection that consolidates information streams rather than fragmenting coordination across multiple platforms. Choose integrated solutions that provide project coordination within single interface.
Establish notification intelligence that respects time zones and work schedules while ensuring urgent information reaches relevant team members promptly. Smart filtering reduces interruption while maintaining coordination effectiveness.
Default to async communication methods that enable thoughtful responses rather than immediate reactions. Reserve synchronous meetings for complex decision-making and creative collaboration rather than routine information sharing.
Create clear communication norms around urgency levels, response time expectations, and appropriate channels for different types of information. Explicit guidelines prevent anxiety while ensuring important coordination doesn't get lost in routine updates.
Ready to streamline your remote team's project management? Try Complex.so free for 14 days and discover how visual-first coordination transforms distributed team productivity. No credit card required, no complex setup—just immediate organization that works across time zones.
Looking for more remote team strategies? Explore our complete guide to small team collaboration tools, discover 5 project management tips specifically for small teams, and learn about building high-performing remote teams. For teams just getting started, check out our 5-minute setup guide.
Complex.so is project management, beautifully simplified for small teams
More in
More in
More in
teams
teams
teams

Teams
Jul 7, 2025
Project Management for Marketing Teams: Campaign Organization Guide
Marketing teams don't fail because of bad ideas—they fail because of chaotic execution. This comprehensive guide shows you how to transform campaign chaos into organized success with marketing-specific project management strategies, tool comparisons, and step-by-step implementation frameworks.

Teams
Jul 7, 2025
Project Management for Marketing Teams: Campaign Organization Guide
Marketing teams don't fail because of bad ideas—they fail because of chaotic execution. This comprehensive guide shows you how to transform campaign chaos into organized success with marketing-specific project management strategies, tool comparisons, and step-by-step implementation frameworks.

Teams
Jul 7, 2025
Project Management for Marketing Teams: Campaign Organization Guide
Marketing teams don't fail because of bad ideas—they fail because of chaotic execution. This comprehensive guide shows you how to transform campaign chaos into organized success with marketing-specific project management strategies, tool comparisons, and step-by-step implementation frameworks.

teams
Jul 2, 2025
How Small Teams Stay Organized Without the Chaos: Task Management Guide
Small teams don't fail because they lack talent, they fail because they lack organization, with research showing that properly organized small teams achieve 21% higher profitability than their chaotic counterparts. This comprehensive guide reveals how to implement the right organizational systems that enhance rather than hinder small team agility, helping teams of 3-20 people coordinate effectively without bureaucratic overhead.

teams
Jul 2, 2025
How Small Teams Stay Organized Without the Chaos: Task Management Guide
Small teams don't fail because they lack talent, they fail because they lack organization, with research showing that properly organized small teams achieve 21% higher profitability than their chaotic counterparts. This comprehensive guide reveals how to implement the right organizational systems that enhance rather than hinder small team agility, helping teams of 3-20 people coordinate effectively without bureaucratic overhead.

teams
Jul 2, 2025
How Small Teams Stay Organized Without the Chaos: Task Management Guide
Small teams don't fail because they lack talent, they fail because they lack organization, with research showing that properly organized small teams achieve 21% higher profitability than their chaotic counterparts. This comprehensive guide reveals how to implement the right organizational systems that enhance rather than hinder small team agility, helping teams of 3-20 people coordinate effectively without bureaucratic overhead.
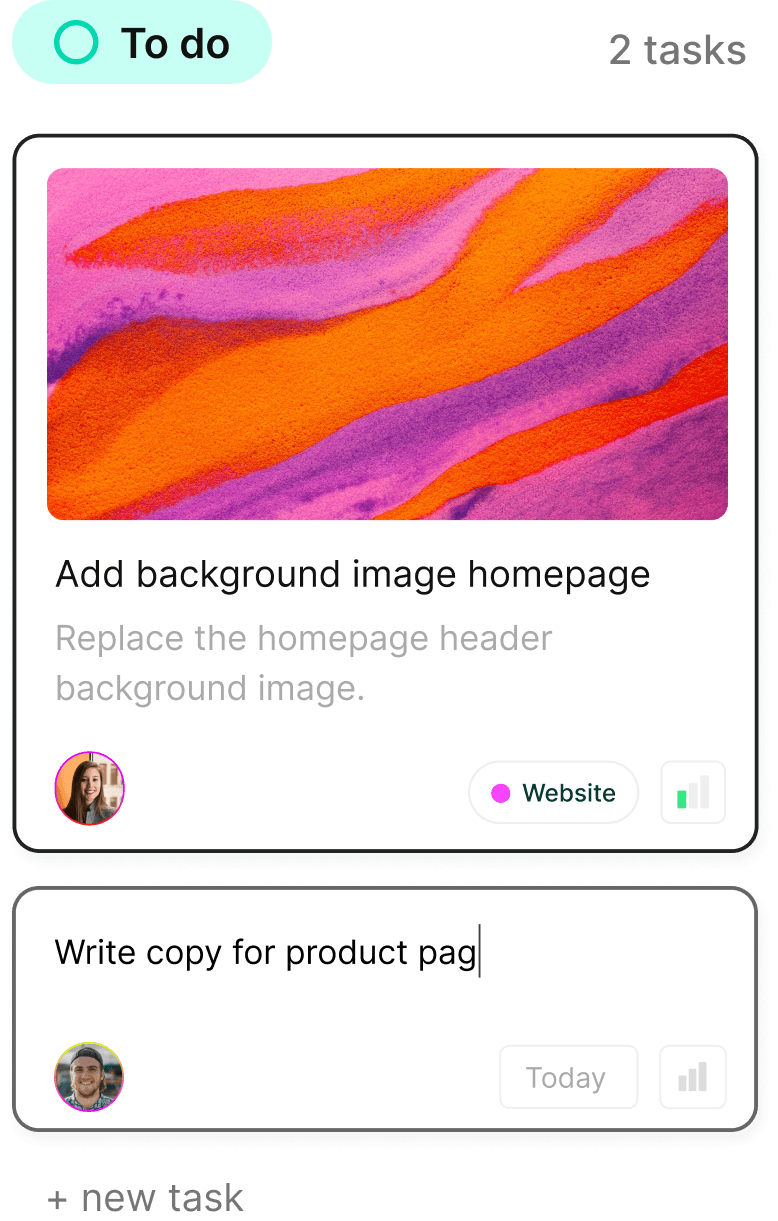

Boost your productivity today—tackle your to-dos like a pro!
Boost your productivity today—tackle your to-dos like a pro!
Boost your productivity today—tackle your to-dos like a pro!
Turn chaos into clarity. Complex.so is here to help you organize your projects, one task at a time.
Turn chaos into clarity. Complex.so is here to help you organize your projects, one task at a time.